So many
products accentuate the low-fat or fat-free benefits now, that it’s almost
scary to eat anything with real fat in it! But the fact is you actually need to
consume fat in order to lose it.

Yes, you
read it right – you need fat to lose fat.
The key is
to consume the good fats instead of bad ones. There are many health benefits in
fat or fatty acids.
Fatty acids
are important for all systems of body to function normally, including your
sknin, respiratory system, circulatory system, brain and organs. There is no
way you can fell and look good by eliminating consumption too low for a long
period of time.
Omega-6 /linoleic, or LA, fat and omega-3
(alpha linolenic or ALA, fat) are so-called essential polyunsaturated fatty
acids (EFAs). Our bodies cannot manufacture these two fats and therefore we
must rely on dietary intake to avoid a deficiency in these essential (for life)
fats. Omega-6 fatty acids are currently overabundant in the typical Western
diet. They are present in corn, safflower, cottonseed, and sunflower oils. If
you look at almost any packeaged food, your’re going to see one of these oils
as an ingredient.

Omega-6 /linoleic, or LA, fat and omega-3
(alpha linolenic or ALA, fat)
are so-called essential polyunsaturated fatty
acids (EFAs).
What is Omega-3 fatty acid?
Omega-3
fatty acid (Alpha linolenic acid) is an essential fatty acid that plays an important role in
brain function and may aid in the prevention of cardiovascular disease. The
American Heart Association recommends a diet in which fatty fish, like salmon
are consumed at least twice a week. Salmon is one of the richest, tastiest,
readily available sources of marine-derived omega-3 fatty acids available to
us. By including wild salmon in your diet, two to four times a week, you should
achieve optimal protection against a multitude of diseases that have been
associated with low intakes of these critical fats.

Omega-3 fatty acid (Alpha linolenic acid) is an
essential fatty acid
You have to
be careful though with fish and choose fish with the lowest mercury content.
Omega-3
fatty acids are found naturally in:
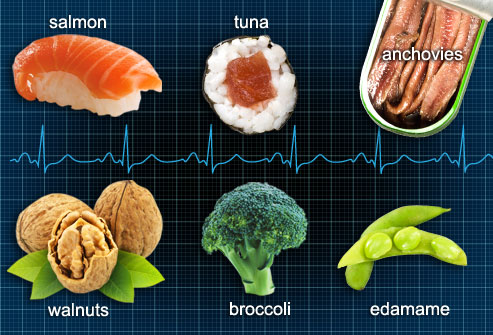
· Grains
· Spirulina
· Brazil nuts
·
Hempseed oil
·
Mustard seeds
· Mustard seeds
· Pumpkin seeds
· Cha seed oil
· Wheat germ oil
· Canola oil (Rapeseed)
·
Green leafy vegetables
· Green leafy
vegetables
· Raw walnuts and walnut
oil
· Flaxseeds or flaxseeds
oil
The
key to EFAs – as with so many health times more omega-6 than omega-3 fatty
acids. This
imbalance determines a myriad of biochemical events that affect our health. For
example, too much omega-6 (the oil dominates our typical diet) issues-is
balance. Your body can’t function optimally without a balanced ratio of EFAs.
The optimum balance of essential fatty acids is a balance of omega-6 to omega-3
that is somewhere between one to one and four to one. Unfortunately, the
typical Western diet contains 14 to 25 promotes and inflammatory state, which
in turn increases your risk for blood clots and narrowing of blood vessels.

The key to EFAs – as with so many health times
more omega-6 than omega-3 fatty acids
We now also
know that without a sufficient intake of omega-3 fatty acids, the body cannot adequately
build an ideal cell membrane. Membranes that are poorly constructed are not
capable of optimizing cellular health, which in turn increases your risk for a
host of health problems, including stroke, heart attack, cardiac arrhythmias,
some forms of cancer, insulin resistance – which can lead to diabetes – asthma,
hypertension, age-related macular degeneration, chronic obstructive lung
disease, autoimmune disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and
depression.