If
you love sports, you must be familiar with trauma. The reasons may be due to
repeated physical impacts, imbalance in biology system, or both. But, if you
practice yoga, it is an effective tool to cure and prevent trauma.
Practicing
yoga frequently will help you keep vitality for your body. Once you get
accustomed to your body through practicing yoga every day with different
movements, you will be more sensitive to your body and be able to recognize the
threat of trauma before the injury really goes into outbreak.
Besides,
yoga has active and passive stretching movements that have useful effect in
preventing trauma. If you do strong and fast intensity sports, muscle bundles
are aqueezed tight and move with small amplitude and limited energy. This makes
you contract trauma more easily while yoga movements does not. Active
stretching movements help your body move and stretch more naturally and
flexibly, which helps to warm up and bend tissues; and passive stretching
movements allow you keep your posture in one minute and relax, which helps
muscles get more stretched. As a result, tissues become more elastic and
resistant, and this makes you recover more quickly from uncomfortable feeling
when you play sports.
This
article presents 3 common kinds of trauma in sports and simple ways to limit
them by yoga. There are plenty of sport traumas which will become chronic, so
if you used to have certain trauma, practice suitable yoga movements to prevent
it becoming chronic disease. If your trauma gets serious and stabbing, you will
have to take rest so as for your inflammation to be relieved. However, if
possible, do some gentle yoga movements since they can help you recover more
quickly. On the days you exercise, do some yoga movements after each practice
session. On the days you take rest, spend 5 to 10 minutes to practice yoga
movements as follows:
1. Foot - Plantar fasciitis
One
of the common traumas related to foot is plantar fasciitis. This is a tissue
layer that connects heel bones with toes and runs along soles. Pressure on
foot’s weaknesses as well as ligament, ankle, and calf stretching can cause
heavy pressure on plantar fascia and creates inflammation. If not being cured,
this inflammation will make heel bones weaker and causes knee pain, hip pian,
and backache.
Common sports: patients of this trauma usually are players of soccer, basketball,
gofl, tennis, and volleyball – sports requiring much running and jumping.
Symptoms: throbbing pain at heel or sole every time you get out of your bed each
morning
Movement instructions: the following movements will help you stretch your
calf and sole to reduce pressure on plantar fascia. Do these movements every
day if you are having or have just got trauma, or practice at least once a week
to prevent this trauma.
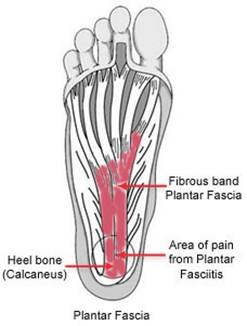
Plantar fasciitis
The first movement: Sole Stretch
This
movement helps gather up muscles and fasciae at sole since it stretches the
thin skin layer of calf muscle, supports toes and foot frame.
Performance method: kneel down, put hands on your knees, and fold your
toes down. Slowly put your hip’s weight back and sit on your soles. To begin
the movement more easily, you can put your hands on the floor and gather part
of weight on them. When you have comfortable and stable posture, sit up and
transmit the whole weight on heels and soles. Keep the posture within 30 to 90
seconds and breathe gently.
The second movement: Reclining
hand-to-big-toe Pose (Supta Padangusthasana)
This
movement helps stretch hamstring and fasciae behind hip, thigh, calf, and sole
muscle.
Performance method: lie supinely on the floor, tie a strip of silk on
the right foot and gradually pull your leg up. Keep your head and shoulders on
the floor and tight hold the silk by both hands. You can bend knee leg but take
notice that the thigh is close to stomach. Keep the posture within 1 to 2
minutes and reverse.
The third movement:
Eye-of-the-needle Pose (Sucirandhrasana)
This
movement helps release pressure of hip – common symptom of athteles who have to
run much but lack foot muscle movement, which makes pressure burden on the back
of foot and causes plantar fasciitis.
Performance method: lie supinely on the floor, put your legs on the wall,
and bend your thighs. Bend the right leg so that ankle of the right leg is on
the left thigh. Massage gently your right thigh by hands. Keep the hip,
backbone, and head on the floor and relax the throat. You can make breathing
movement become more difficult or easier by moving near or far from the wall.
If you want to practice at stronger intensity, put your hand below the right
ham and stretch your body. Keep the posture within 1 to 2 minutes and reverse.
2. Knee - Iliotibial band syndrome
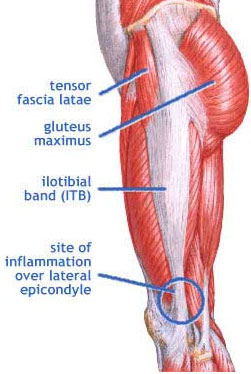
Iliotibial band
syndrome
One
of the common knee traumas in sports is the stimulation of iliotibial (also
called IT) – a kind of ligament in fascia, running from the top of external hip
to below thighs. We are often mistaken that stretching IT will help it get back
to normal, but in fact, IT is made up from fibre, and reason of the syndrome
depends on muscles around. Usually, thigh muscles connecting closely to IT will
be tightened, which cause pressure on IT. The IT may also lose ability to slide
on thigh muscles (these muscles can regulate thighs’ movements). In this case,
jogging or walking can cause rub, make the muscles become hard, more tightened
to knee, and cause the pain.