Your 13th Week
For most women, any
discomforts of early pregnancy start to disappear this trimester. The
high levels of pregnancy hormones, which are thought to contribute to
sickness, are subsiding, and fatigue should begin to diminish.
Meanwhile, your baby floats peacefully in the amniotic sac. As he goes
on growing, so the sac will expand to give him plenty of room to kick
and stretch. His brain is developing at a rapid rate.
NOTE
As you enter this second trimester, your body will settle down to pregnancy
You are 12 Weeks and 1 Day 195 days to go…
This is a good time to start telling the important people in your life your exciting news—before they guess for themselves.
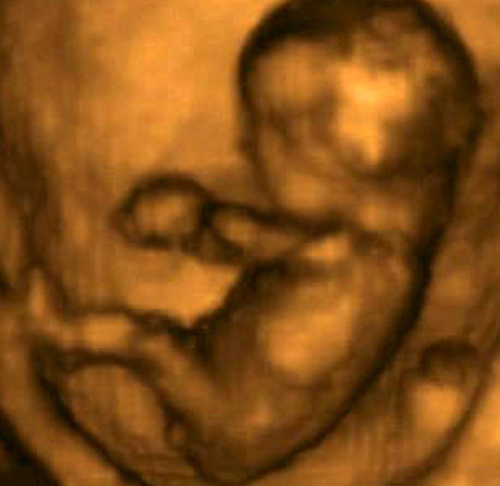
Your baby today
This 3D ultrasound scan clearly demonstrates that the baby’s
arms and legs are now fully formed and much more in proportion with the
trunk. All of the baby’s joints are now formed, enabling a full range of
movement.
Now that you’re in your second trimester and have had your dating scan ,
you may want to start telling a wider circle of people that you’re
pregnant. You can feel confident doing this, knowing that the risk of
miscarriage is reduced to no more than 1 percent after the 12th week.
Besides this, your belly will begin to show in a few weeks, if it hasn’t
already, so hiding the pregnancy will become difficult.
If you and your
partner have been keeping the pregnancy a secret for the past three
months, announcing it will be a huge release and it can be a positive
experience to share the news with others. However, be prepared for an
onslaught of advice and people’s tales of their pregnancy and birth
experiences!
Sometimes letting
others know that you’re pregnant can be difficult. Be sensitive to other
people’s feelings: friends who also want to be parents, but are having
difficulty conceiving, may find it difficult to share your happiness
right away. It’s preferable to tell these people face to face rather
than them hearing it through the grapevine. Even if they don’t react
positively, and don’t want to talk about your pregnancy all the time,
give them time to come to terms with it at their own pace. Remember they
can be sad for themselves while being happy for you.
Second trimester tests
If you haven’t had a nuchal translucency scan, blood tests will be offered this trimester to screen for Down .
The triple test is done at 16–18 weeks. It measures levels of the hormones hCG, AFP, and estriol.
The quadruple test is done at 15–22 weeks. It measures levels of inhibin A in addition to the hormones measured in the triple test.
… Your body
Become a clothes cheat!
Although your clothes may be feeling a little tight by this stage,
you probably aren’t ready to wear voluminous maternity clothing just
yet, so it’s time to get creative! Simply bridge the gap between your
button and button-hole with an rubber band (see image)
or by sewing in an elastic panel. Assuming he’s bigger than you, try
raiding your partner’s wardrobe—his T-shirts, shirts, and sweaters can
be ruched in with a low-slung belt.
Check what’s in
your wardrobe already: empire-cut dresses will see you through most of
your pregnancy; looser smock tops can be layered over tight-fitting
T-shirts; low-slung pants can sit neatly under your belly, topped with
an oversized shirt. The one item you might want to purchase is a pair of
maternity pants—something stretchy with an adjustable waist.
Diagnostic Tests
If you’ve had a positive
screening test for Down syndrome or another genetic abnormality, you
will be offered a diagnostic test, which gives a definitive answer as to
whether or not your baby has an abnormality.
What are diagnostic tests?
Diagnostic tests are
tests that involve taking a sample of either the placenta, the amniotic
fluid, or fetal blood. The samples are then sent away and examined in a
laboratory for chromosomal or genetic abnormalities. The two main
diagnostic tests are amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling, or
CVS. Since both of these tests carry a small risk of miscarriage (see Chorionic villus sampling), you will need to carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages of the tests before going ahead with either of them.
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
Chorionic villi are
fragments of placental tissue. Because the placenta originates from the
fertilized egg, the chromosomes in the cells that make up the placenta
are representative of your baby’s chromosomes. During CVS, a small
amount of tissue from your placenta is removed and tested in a
laboratory to reveal if your baby has a chromosomal disorder such as
Down syndrome or another trisomy disorder, such as trisomy 18. CVS is
done between 10 and 121/2 weeks’ gestation and the results are usually
available within 7 to 10 days. The procedure can also definitely
identify your baby’s sex, if you want to know. If you don’t want to have
this information, make your wishes clear before the test. In rare
cases, the doctor will be unable to perform CVS due to the placenta’s
position. In this case, you may be asked to return for an amniocentesis
at 15 weeks.
Amniocentesis
This is the most common
diagnostic test, done at around 15 to 19 weeks of pregnancy. The
amniotic fluid around your baby mainly consists of your baby’s urine and
contains cells from your baby’s skin and urinary tract. During
amniocentesis, a number of cells are collected from the amniotic fluid.
They are then sent to a laboratory and grown in a cell culture, until
there is a sufficient number of cells to examine your baby’s chromosomes
and identify whether your baby has a chromosomal abnormality such as
Down syndrome. Amniotic fluid can also be tested for high levels of the
substance alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), which could mean that your baby has a
neural tube defect such as spina bifida or anencephaly. Other DNA
testing can also be done during amniocentesis to check for congenital
conditions that may run in either parent’s family. .
How you might feel
You may be
concerned about the idea of a needle going through your abdomen, or a
catheter into your cervix; however, the majority of women find that
these procedures are not particularly painful. If you are having a
transabdominal procedure, the needle usually doesn’t hurt any more than
it does when you are having a blood test. Some doctors use a small
amount of local anesthetic before the transabdominal procedure to numb
the area, although the anesthetic itself can occasionally sting.
Although afterward it’s common to experience uterine cramps, similar to
the cramps you feel during menstruation, rest assured that these cramps
alone do not mean that you have an increased risk of miscarriage.
If your blood type is Rh negative
you should receive an injection of anti-Rh after the procedure to
prevent complications from occurring during this and future pregnancies.
After the procedure
It’s generally
thought that being active after CVS or amniocentesis does not increase
your risk of miscarriage. However, you may feel better if you don’t
exercise heavily right away; it’s not necessary to remain in bed. In
most cases, you should be physically able to return to work within a day
or so after a diagnostic procedure, although some women may feel
emotionally fragile and may not feel up to returning to work right away.
Getting the results
Usually, chromosomal
results from diagnostic tests take around 1–2 weeks to return, and
sometimes may take as long as three weeks. If you have had your AFP
level tested with amniocentesis (see Amniocentesis),
the results for this are usually available fairly quickly, after around
1–3 days. If you are considering terminating your pregnancy based on
the results of a diagnostic test, opt for testing earlier in the time
frame during which it is offered, rather than later, to reduce risks of
complications.
Chorionic villus sampling
There are two ways of doing chorionic villus sampling.
In the transabdominal method, a fine needle is placed through the
abdomen to collect placental fragments. In the transcervical procedure, a
thin tube (catheter) is inserted into the cervix. The method used
depends on the position of the placenta and the doctor’s training and
expertise. During the procedure, ultrasound guidance is used so that the
doctor can see the placenta’s position.
CVS can also
be done in a multiple pregnancy; in this case both the transabdominal
and transcervical methods of collection may be used.
Transabdominal procedure
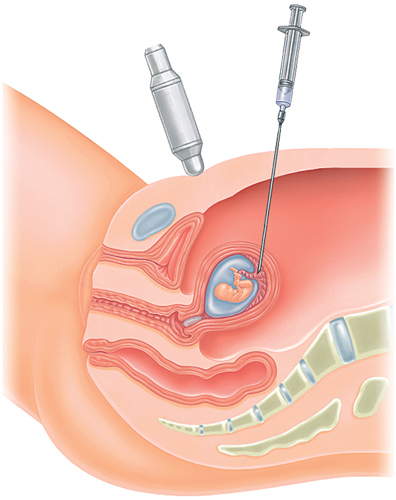
Transcervical procedure
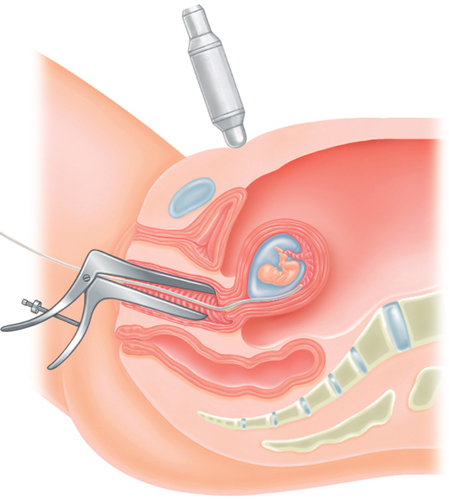
When to worry
If, following the procedure, you experience severe abdominal pain,
fever greater than 100.5° F (38° C), vaginal bleeding, or a large gush
of clear fluid from your vagina you should call your doctor immediately.
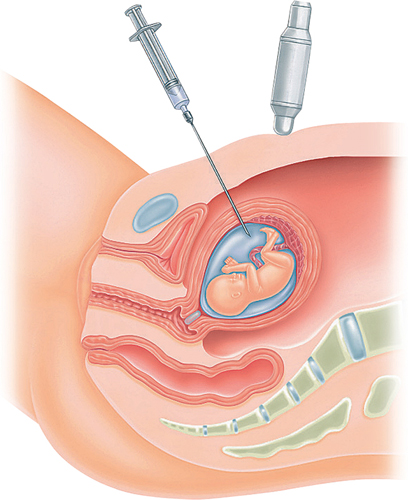
Amniocentesis
During amniocentesis, the doctor uses ultrasound to locate
an open pocket of amniotic fluid. Under continued ultrasound guidance, a
thin needle is placed through the skin of the abdomen and then through
the uterus and into the amniotic fluid. A small amount of the fluid is
drawn up into the needle and an attached syringe. A local anesthetic may
be applied to your abdomen before the procedure to ease any discomfort.
Comparison of CVS and amniocentesis
Before deciding on a
diagnostic test, you may want to weigh their pros and cons. Consider too
that the risks may be reduced with a doctor who has expertise in a
particular test.
CVS: the pros
CVS
can be done up to five weeks earlier than amniocentesis, so if an
abnormality is found and you decide to terminate, this can be done in a
safer, less traumatic way.
Since more genetic material is collected, the results may arrive sooner, decreasing the anxious wait.
If
you’re nervous about a needle going into the abdomen, transcervical CVS
means that you can avoid this but still have a prenatal diagnosis.
CVS: the cons
The
risk of miscarriage after CVS is similar to amniocentesis, at around 1
in 400. The miscarriage rate is the same whether it’s done
transabdominally or transvaginally.
In
the past, some women had CVS then had babies with limb abnormalities.
It’s now thought that most of these cases occurred when CVS was done
before 10 weeks when the limbs were starting to form.
Amniocentesis: the pros
Amniocentesis: the cons
Since
this is done later than CVS and the results take longer, if you
terminate you may be offered an induction for vaginal delivery, but most
doctors can perform D&E until 20 to 24 weeks depending on the
state.