You may know in advance that a condition or factor in
your pregnancy means that intervention, such as an induction or a
cesarean section, will be needed. At other times, events can occur in
labor that mean assistance is needed, or a premature labor can mean that
your baby needs special care. In all cases, rest assured that
procedures are in place to ensure your own and your baby’s safety.
NOTE
Each labor is different and there are times when some type of intervention is needed

Premature Birth
The term “premature”
describes both the time of birth, before 37 weeks, and how well prepared
your baby is for life outside of the uterus. Premature births account
for 12.7 percent of U.S. births.
Your baby may be born prematurely either because an early delivery is advised on medical grounds (see Advising an early delivery),
or you go into spontaneous preterm labor. The earlier the birth, the
higher the chance of complications in the baby, such as breathing
problems or infections. Nowadays, however, huge advances in the care of
premature babies means that babies born as early as 23 or 24 weeks may
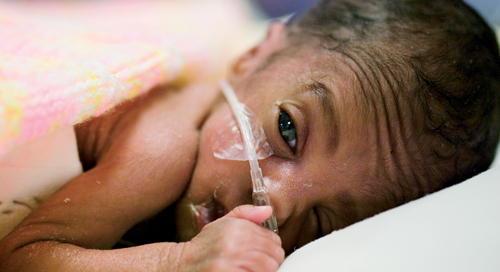
survive. If your baby is premature, he may need to spend time in a
neonatal intensive care unit .
Seeing your tiny baby hooked up to monitors and tubes can be alarming, but take comfort from the fact that these are helping your baby to breathe and feed and in turn to develop.
Advising an early delivery
A decision may be made to
deliver a baby early if the mother’s or baby’s health is in danger. For
example, an early delivery may be recommended if the mother has a
medical problem, such as a heart condition that could increase her
physical stress, or preeclampsia,
which could endanger her own and her baby’s health. An early delivery
may also be advised if a scan shows that the placenta is not functioning
well and the baby is not receiving enough oxygen. Forty-seven percent
of babies in the US delivered before 32 weeks are born by cesarean, as
are about a third of babies born between 34 and 36 weeks.
Spontaneous preterm labor
The cause of spontaneous
labor before 37 weeks is often unknown. However, it is more likely if a
woman has a major abnormality of the uterine wall, such as large
fibroids ,
a weakness in the cervix, which may have been present from birth, or
have occurred after surgery to the cervix or is pregnant with more than
one baby. Infections like bacterial vaginosis can also set off
contractions at an early stage.
What might be done?
Preterm labor can’t be stopped, but medication can slow the process and reduce some risks.
Steroids can
promote the production of a natural chemical in the baby’s lungs that
reduces the effort of breathing. They must be given 24 to 48 hours
before the birth to have maximum benefit.
You may also be given
oral medicine or an injection to reduce the frequency of contractions.
This can prolong pregnancy for a few days, during which time the
steroids can take effect. Also, if necessary, you can be transferred to a
hospital with NICU facilities.
Finally, you may be
advised to have injected antibiotics since preterm babies are
susceptible to bacterial infections caught via the cervix during birth.
Predicting premature labor
It’s hard to predict
who will go into labor prematurely. However, if you’ve had a previous
preterm birth, tests may be done to find out if it is likely in your
current pregnancy. A cervical scan may be done around 23 weeks since a
shorter cervix increases the risk of early labor. Pelvic swabs detect
bacteria that are linked to preterm labor, and “fetal Fibronectin” test
between 24 and 34 weeks shows whether a protein is present that, during
the second half of pregnancy, generally can’t be detected until 1–3
weeks before labor and delivery. Sometimes, a short cervix is
strengthened with a stitch. Antibiotics can be given if abnormal
bacteria are found. Progesterone may be given to stop contractions.
Induction of Labor
For 22.3 percent of women in the US, labor is started by artificial means, or induced, to reduce the risks to mother and baby.
An induction may be
offered if it’s felt that continuing the pregnancy poses a risk to your
health or to the health of your baby. The most common reason for an
induction is the continuation of a pregnancy beyond 41 or 42 weeks, in
which case the placenta may begin to fail. Induction may be offered
earlier if you have twins, or a medical condition such as diabetes.
Before setting a date for induction, your doctor may offer to strip your
membranes to help you go into spontaneous labor.
Induction is not
the same as an augmentation of labor, which is when drugs are used to
increase the efficiency of your contractions when you’ve already gone
into labor spontaneously .
Assessing the cervix
Before an induction,
you’ll have an internal examination to assess the cervix. Induction is
easier if your cervix is short and soft, described as “favorable” or
“ripe,” rather than long and firm. The findings may be logged in a table
called the Bishop’s Score, which also assesses how far the cervix is
dilated , the position of the cervix, and the station of the fetal head in the pelvis . A total score over six indicates good conditions for an induction of labor.
Softening the cervix
If your cervix isn’t ripe,
it can be softened with prostaglandins. These are naturally occurring
chemicals that help stimulate contractions. Artificial prostaglandins
can be given in the form of vaginal tablets of gel, which are placed at
the top of the vagina near the cervix, or a vaginal suppository or an
oral pill. This is usually effective, but sometimes prostaglandins fail
to soften the cervix and may be tried again after a few days. On the
other hand, some women experience dramatic effects after a small dose.
Breaking the water
Amniotomy, or
artificial rupture of the membranes (ARM), is one of the most important
steps in the induction process, often referred to as “breaking the
water” and it’s done once the cervix is soft and slightly dilated, and
the head has started to enter the pelvis. A thin plastic probe is passed
through your cervix and used to make a small hole in the amniotic
membranes, which allows some of the fluid around your baby to leak out.
This softens the cervix even more and can provoke contractions in the
muscular wall of the uterus. If contractions don’t become established
after ARM, then you’ll require treatment with Syntocinon or Pitocin (see
Oxytocin, Syntocinon, Pitocin).
Oxytocin, Syntocinon, Pitocin
Oxytocin is a
natural hormone that stimulates the uterus, increasing the frequency and
strength of contractions. A synthetic form, Syntocinon or Pitocin, is
used with the same effect. It’s diluted in fluid then dripped into a
vein in your arm or injected into a large muscle. This is safe and
effective when used correctly; however, it must be used with care since
excessive contractions can reduce your baby’s oxygen supply in labor.
Your contractions and your baby’s heartbeat will be continuously
monitored .
| Q: |
Are medical interventions more likely with an induction?
|
| A: |
If your labor is induced, the chance that you will need an assisted delivery with forceps or vacuum
or a cesarean is increased. This is even more likely if you are having
your first baby, if the cervix is unfavorable, or if you’re being
induced relatively early in your pregnancy. The reason for these medical
interventions is usually that the labor is proceeding too slowly, or
that it cannot be started at all, despite all of the steps taken. Also,
concerns about the baby’s well-being during the induction process can
sometimes lead to intervention.
|
| Q: |
Is induction of labor more painful than a spontaneous labor?
|
| A: |
Some women find that they experience strong contractions very
quickly after an induction. Since they haven’t been able to build up
gradually to more painful contractions, they may be less able to
tolerate the pain, which can result in an increased need for stronger
types of pain relief such as an epidural.
|