This is Day 4 of your Menstrual Cycle 276 days to go…
Like many women, you may sometimes feel ruled by your hormones, and it helps to understand why they fluctuate.
What’s happening inside
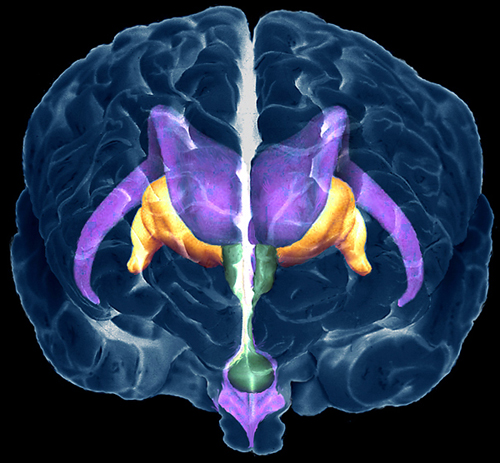
In this color 3-D scan of the human brain, the green central
structure is the hypothalamus. This controls emotions and body
temperature, and releases chemicals that regulate the release of
hormones from the pituitary gland (green circle at bottom).
The hormone build-up to ovulation
starts right now in week one of your menstrual cycle. Your pituitary
gland, which lies in the base of your brain, produces
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). During your period, the level of FSH
rises steadily, triggering the development of the follicles (around
15–20 each month) in each ovary. As well as containing each egg, the
follicles produce estrogen.
The hormone estrogen
circulates, affecting the pituitary gland and causing it to produce
luteinizing hormone (LH)—this triggers ovulation (see This is Day 14 of your Menstrual Cycle). This week your estrogen levels are low and steady, but will rise dramatically later in your cycle.
Progesterone levels
are low during your period, but start to rise several days afterward and
stay high for the second part of the cycle. Under the influence of
progesterone, the muscles in the cervix relax, easing open the cervical
canal. Changes also affect the mucus, which becomes more fluid, so sperm
find it easier to swim through. It is progesterone that enables the
lining of the uterus to thicken in preparation for implantation of the
fertilized egg.
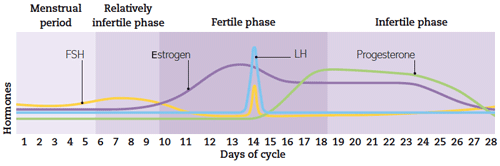
Changes during the menstrual cycle
There are four hormones at work
during the menstrual cycle: FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) causes
the egg follicles to start developing in the ovary; estrogen is produced
by the developing egg and peaks just before ovulation; LH (luteinizing
hormone) triggers ovulation; progesterone thickens the lining of the
uterus.
Men get PMS too!
Scientists have
confirmed there’s a male version of PMS—Irritable Male Syndrome. Mood
swings, temper tantrums, and loss of libido in men were found to be
caused by falling levels of testosterone due to stress.
Fertility rites
Rooted in folklore, these fertility tips require a leap of faith and a good sense of humor!
Use the moon.
Exponents
of “lunaception” believe that women whose menstrual cycle aligns with
the lunar cycle—so they menstruate during the new moon and ovulate when
the moon is full—have more chance of conceiving. It’s based on the
theory that women’s cycles are influenced by natural light.
Dance around the Maypole.
Maypoles are thought to herald the arrival of spring and celebrate fertility.
This is Day 5 of your Menstrual Cycle 275 days to go…
Making some lifestyle changes is essential when you’re trying to get pregnant and cutting down on alcohol is a good start.
What’s happening inside
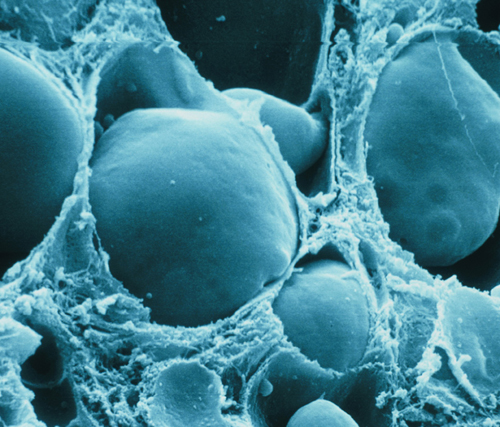
This cross section through the ovary shows several ovarian
follicles. Between each follicle, the connective tissue can be seen.
Each month about 15–20 follicles mature, but it is usually only one that
will fully mature and release an egg.
Even though it’s still the week of your period,
and some time before you ovulate, try to ensure you’re in the best
possible health to maximize fertility. One way is to cut down your
alcohol intake.
Heavy drinking can
reduce the chances of conceiving and, if you do get pregnant, it can
also harm your unborn baby’s development. There is plenty of evidence
that drinking beyond the recommended amounts is harmful. What’s lacking
is evidence of the effects on conception and pregnancy of the occasional
alcoholic drink. There is no known safe level of alcohol consumption
for pregnant women. However, many women decide to err on the side of
caution and stop drinking alcohol entirely while trying to conceive and
in early pregnancy. Some find that morning sickness (see You are 5 Weeks and 3 Days) naturally reduces desire for alcohol.
Alcohol also affects male
fertility. It has adverse effects on the quantity and quality of sperm
produced, and drinking large amounts can cause impotence.
You may find a drink
helps you and your partner relax and puts you in the mood for sex,
thereby increasing your chances of conception, but you may want to
rethink having the occasional glass of your favorite tipple. The US
Surgeon General recommends that women trying to get pregnant abstain
from alcohol to eliminate potential problems.
Opt for nonalcoholic drinks if you’re trying to get pregnant. A high intake of alcohol can adversely affect your chances of conceiving.

Illicit or “street” drugs can harm your unborn baby.
You should try to
stop using drugs before you conceive. However if you regularly use
drugs, or find it hard to manage without them, it is essential to get
medical support. Ask your doctor for advice. He or she will be able to
help and put you in touch with a support group.
Medical checkups
Before you try to conceive, speak to your doctor about the following tests:
Rubella:
have a blood test to check that you have antibodies against rubella
(German measles). Being infected by the rubella virus for the first time
in early pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of the baby
developing an abnormality, and increasing the risk of miscarriage. If
you were vaccinated against rubella as a child, your antibody level may
be high enough to protect your baby. If it isn’t high enough, you’ll be
offered a MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccine and advised not to
conceive for three months.
Sexually transmitted infections:
go to your doctor for tests to rule out infections such as chlamydia,
genital warts, and herpes. You may also want to consider having an HIV
test at your as well. Women with HIV can still bear children, but may be
prescribed a medicine to reduce the chances of passing the infection to
their child. A cesarean may be recommended.
This is Day 6 of your Menstrual Cycle 274 days to go…
Eating well is an essential part of conception and pregnancy so you and your partner should get into good habits now.
What’s happening inside
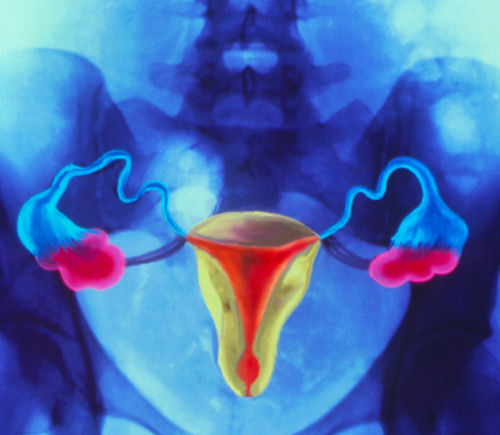
In this artwork of the uterus, the green central structure is
the pear-shaped uterus itself; the red part is the cavity of the uterus.
The blue structures to either side are the fallopian tubes, which each
have an ovary, seen in pink here, at the end.
Take the time in this first two weeks of your cycle, before you ovulate, to look at what you eat on a daily basis—if you and your partner (see Dads: your diet counts too) make some simple changes to your diet, it might just improve your chances of conception.
Use this opportunity to check your weight ie your Body Mass Index (BMI)since a BMI of under 19 or over 24 could adversely affect fertility.
If you’re
overweight, excess fat tissue may affect your metabolism and hormones
and you may not ovulate as regularly, or at all. If you need fertility
treatment, the chances of success are also lower if you’re overweight,
because you may respond less well to the drugs that stimulate ovulation.
Once you’re pregnant, being overweight can also cause an increased risk
of complications, decreasing the chance of carrying the pregnancy to
full term.
Weighing too little when
you’re trying to conceive isn’t healthy either. Pregnancy takes its
toll on a woman’s reserves, so a little stored fat is a good thing for
mother and baby. Being seriously underweight can affect ovulation and
make periods irregular or absent, and conception unlikely.
Your BMI when you conceive is also a good indication of how much weight you should gain once you’re pregnant, so it’s worth getting it checked at this point.
… Nutrition
Vital B vitamins
Your diet should include foods containing B vitamins. Take a pregnancy multivitamin if needed.
B1 efficiency has been linked to failed ovulation and implantation.
B2 deficiency has been linked to infertility and miscarriage.
B5 is important for conception and fetal development.
B6 is essential for the formation and functioning of sex hormones.
B12, with folate, is essential to fetal development.
Get fit and fertile!
Regular exercise can increase your chances of conceiving
by allowing your body to work at optimum levels. If you’re fit and have
a healthy lifestyle, you will reduce the level of toxins in your body
and be less stressed, which makes it easier to conceive. Exercise will
also regulate your energy and your blood-sugar levels, which assists the
body in regulating the hormonal cycle—a key player in the reproductive
process. Conversely, overexercising can adversely affect the ovulation
process and make conception more difficult.
The guidelines for
exercising at this crucial time of conception are to continue
weight-bearing exercise, such as walking, running, or aerobics, for 30
minutes five times a week at a moderate intensity. It is important to
listen to your body—moderate means exercising within a comfortable
range, where the exercise isn’t too hard but is pushing your body enough
to feel the benefits.
