There are many diseases that include
mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding.
There are many diseases that include
mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding… The
important thing is that they have to be early detected in order to have timely
treatment for future mothers and avoid transmitting to babies.
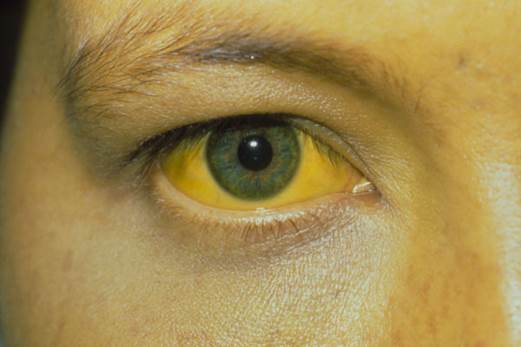
Hepatitis
B is one of those infectious diseases.
Hepatitis B
Filterable B virus is a kind of viruses
that is liver-directed. There are many ways that filterable B viruses can be
transmitted from one to others, such as: mother-to-child transmission (the most
important one), sexual transmission (the disease can be transmitted by the
sexual or homosexual activities), blood or blood product transmission. Besides,
if you are infected with the secretion of people who have the hepatitis B
virus, or use the same injection needle that they used, you can have yourself
suffered from hepatitis B, too.
Mothers who have hepatitis B before getting
pregnant can transmit the virus to their children during pregnancy. The risk of
transmitting the disease to the fetus can be up to 90% if there’s no protecting
methods applied after birth. That is because the baby’s immune system, at that
time, cannot produce resistance, so the baby tends to be infected with the hepatitis
B virus.
While 90% of adults who have B hepatitis
completely immune to the disease when they reach adulthood, and only 10% of
them have chronic infection, children infected with B hepatitis virus from
birth are just the opposite; 90% of these children will have chronic infection.
This stage lasts for years and may not have the clinical manifestation, but in
the end, it’ll lead to severe effects, such as cirrhosis, liver cancer…

The
mother-to-child disease can be transmitted while breastfeeding.
In order not to transmit the hepatitis B
virus to children, first of all, mothers who have hepatitis B must have their
disease stabilized before getting pregnant and have their children vaccinated after
birth. In addition, children can have an infection of anti-hepatitis B serum or
vaccine, or both. The anti-hepatitis B vaccinating has to be in immunization
schedule.
HIV infection
Mother-to-child transmission is one of the
3 HIV transmission modes. Mothers who have HIV can transmit the HIV virus to their
children in 3 periods: pregnancy, delivery, and breastfeeding.
During
pregnancy

At
the time the fetus is in the 18th week, the rate of HIV transmitting
through placenta is quite high.
HIV is a mother-to-child disease: the
mother’s blood, through placenta, goes into the fetus’s body. The HIV
transmission during pregnancy can occur as soon as the fetus in its 8 weeks old
and lasts to the end of pregnancy. However, it’s realized that at the time the
fetus is in the 18th week, the rate of HIV transmitting through
placenta is quite high. About 20-30% of children who are infected with HIV
virus from birth are considered to be transmitted through placenta. This rate
can increase, in other words, the risk of HIV transmission through placenta
increase depends on the mother’s age’s increase or the moment that the mother
is infected with HIV virus; if she is infected with HIV virus during pregnancy
in which the level of HIV virus in blood is very high, the risk will increase.
Similarly, if the mother is in the late stage of HIV which is AIDS, and get
pregnant, the risk will increase, too.
During
childbirth
Although there is certain percentage of
children who are infected with HIV from birth, many studies show that the
mother-to-child transmission of HIV often occurs late, during childbirth or at
the time the child passes through the mother’s genital tract, it is directly
interfered with the mother’s vaginal discharge or blood. That is because, when
labor starts, the amniotic fluid, matrix fluid, and vaginal fluid will
penetrate into the child. The HIV can transmit from the vaginal ulcers to the
infant’s body. It’s also believed that the strong uterine contractions can push
the blood that is infected with HIV to the child’s circulation.
About 50-60% of children infected with HIV
from the mother are considered to have HIV transmission during labor. In
difficult delivery cases, the labor lasts longer, the mother’s soft part is
damaged, the baby is scratched or has trauma, which all increase the HIV
transmission risk in children.