While
breastfeeding
Though the level of HIV virus in breast
milk isn’t high, the HIV virus can penetrate into baby’s oral mucosa, tongue
and gums, causing infection, especially when the baby has oral inflammations.
In the case the mother’s breasts have inflammations, scratches or the baby’s
teeth cause mother’s breast bleeding, HIV virus will follow the blood flow and
penetrate into the oral mucosa, causing HIV infection. About 20-30% of children
have mother-to-child HIV transmission due to breastfeeding; it depends on the
time and breastfeeding methods.
The risk of being infected with HIV by
breastfeeding increases when the mother comes to the AIDS stage (the level of
HIV virus in blood is high) or she is infected with HIV after giving birth or
during the breastfeeding period, (in the early stage of HIV, the level of HIV
virus in blood is quite high, too); the longer the mother feeds the baby with
her breast milk, the bigger the risk of HIV transmission gets. In addition, it
will also happens to the HIV mother who concurrently feeds her child with her
breast milk and other foods (the different foods and drinks can cause diarrhea,
intestinal mucosa injury, which helps the HIV virus transmit more easily from
the mother’s milk to the child)

The
risk of being infected with HIV by breastfeeding increases when the mother
comes to the AIDS stage.
For that reason, to prevent and reduce the
risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV, the mother infected with HIV virus
needs to go to the specialized medical facilities to receive professional advice,
pregnancy care and prophylactic treatment for the mother-to-child HIV
transmission as well as to be kept in track with the health state. During
delivery, the HIV- infected mother needs to continue following the
obstetrician’s instructions in order to have a smooth and safe birth giving.
Moms should ask for doctor’s advice about child caring and follow his care and
treatment instructions.

You
should have regular medical examinations to prevent diseases infected from
mothers to children.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is caused by Neisseria gonorrhea
virus. This virus often lives in the wet part of the body like vagina, penis,
eyes, throat and rectum. The gonorrhea can be transmitted by every form of sex,
such as oral sex, vaginal and anal sex.
The gonorrhea symptoms of female is not
typical, it silently develops and hardly has acute symptoms.
Pregnant women who don’t know that they
have gonorrhea or know but have unfinished treatments can transmit the disease
to their children. The child’s infected with the gonorrhea virus during labor
when it interferes with the mother’s vagina. In that case, the newborn can have
eye conjunctivitis which is the most popular disease.
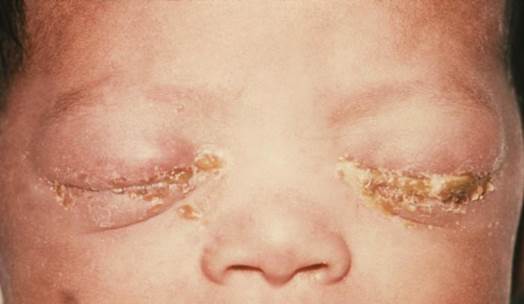
The
symptoms often appear in the third day after birth and happen to 2 eyes.
The symptoms often appear in the third day
after birth and happen to 2 eyes. They are eyelid deformation, edema, eyelid
sticking, greenish-yellow plus secreting, sensitivity to light and bleeding. If
there’s no treatment applied, it can cause ulcer complication, corneal
perforation and blinding. Sometimes, the child can be transmitted the gonorrhea
and Chlamydia virus from the cervical secretion.
Besides, if the gonorrhea patients aren’t
received treatment before getting pregnant, it can lead to pelvic inflammatory
disease – PID. This is the reason causing ectopic pregnancy which increases the
risk of miscarriage and other complications that can put the child’s life in
danger.
So, pregnant women who are likely to have
gonorrhea (have lots of partner, have sex with sick people without protection)
need to take medical exams to have the situation controlled and take another
one in around 3 last months of the pregnancy to limit the complications of the
disease. The disease can be easily treated, so you should consult a doctor if
you are in the possible group or have gonorrhea symptoms.