3. How Your Baby Is Growing and Developing
Intrauterine-growth restriction (IUGR) indicates a fetus is small for its gestational age. Weight is below the 10th percentile (in the lowest 10%) for the baby’s gestational age. This means 9 out of 10 babies of normal growth are larger.
When dates are correct and the pregnancy is as far along as expected and weight falls below the 10th percentile, it’s cause for concern. Growth-restricted babies can have problems.
Your healthcare provider measures you at
each visit to see how your uterus and baby are growing. A problem is
usually found by measuring the uterus over a
period of time and finding little or no change. If you measured 10¾
inches (27cm) at 27 weeks gestation and at 31 weeks you measure only 11
inches (28cm), there might be concern about IUGR, and tests may be
ordered.
What causes IUGR? Many conditions can
raise the risk of IUGR. We know a woman who has delivered a
growth-restricted baby may be more likely to do so again.
Anything that results in baby receiving
less nutrition can be a factor. Lifestyle choices can cause IUGR, such
as smoking. The more cigarettes smoked, the smaller the baby. Alcohol
and drug use can also restrict growth.
A woman who doesn’t gain enough weight
may have a growth-restricted baby. When you eat fewer than 1500
calories a day for an extended time, IUGR may result. So eat a
healthful diet during pregnancy. Don’t restrict normal weight gain.
Pre-eclampsia and high blood pressure can
have an effect on baby’s growth. Some infections in mom may restrict
growth. Anemia may also be a cause.
Women who live at high altitudes are more
likely to have babies who weigh less. Carrying more than one baby may
also cause smaller-than-normal babies.
Other reasons for a small baby, unrelated
to IUGR, include the fact a woman who is small might have a small baby.
In addition, an overdue pregnancy can lead to a smaller baby. A baby
with birth defects may be smaller.
Detecting IUGR is one important reason to
keep all your prenatal appointments. You may not like being measured
and weighed at every appointment, but it helps your healthcare provider
see if your pregnancy is growing and baby is getting bigger.
IUGR can be diagnosed or confirmed by
ultrasound. Ultrasound may also be used to assure baby is healthy and
no malformations exist that must be dealt with at birth.
When IUGR is diagnosed, avoid doing
anything that could make it worse. Bed rest is one treatment. Resting
on your side allows the baby to receive the best blood flow, and better
blood flow is the best chance it has to improve growth. If maternal disease causes IUGR, you need to be treated to improve your health.
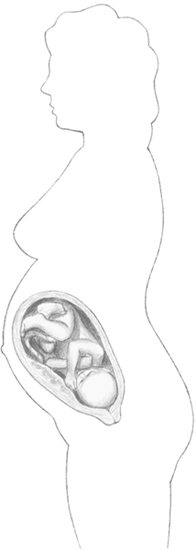
Comparative size of the uterus at 31
weeks of pregnancy (fetal age—29 weeks). The uterus can be felt about
4½ inches (11cm) above the bellybutton.
An infant with IUGR
is at risk of dying before delivery. Baby may need to be delivered
before it is full term. Infants with IUGR may not tolerate labor well;
a Cesarean delivery may be necessary. The baby may be safer outside the
uterus than inside of it.
Dad Tip
It’s time to start looking for
baby equipment, such as cribs, car seats and layette items. You’ll need
to make some of these purchases before baby’s birth. Most hospitals or
birthing centers won’t let you take baby home without an approved car
seat.