3. How Your Baby Is Growing and Developing
Twins? Triplets? More?
The rate of multiple births is going
up—since 1980, the rate of twin births has increased 70%. Statistics
show that close to 4% of all births in the United States are multiple
births. If you’re expecting more than one baby, you’re not alone!
When talking about pregnancies of more
than one baby, in most cases we refer to twins. The chance of a twin
pregnancy is more likely than pregnancy with triplets, quadruplets or
quintuplets (or even more!). However, we are seeing more triplet and
higher-order births. A triplet birth is not very common; it happens
about once in every 7000 deliveries. (Dr. Curtis has been fortunate to
deliver two sets of triplets in his medical career.) Quadruplets are born once in every 725,000 births; quintuplets once in every 47 million births!
No matter how it happens, being pregnant
with two or more babies can affect you in many ways. Your pregnancy
will be different, and the adjustments you may need to make may be more
wide-ranging. These changes may be necessary for your health and the
health of your babies. Work closely with your healthcare provider to
help make your pregnancy healthy and safe.
A multiple pregnancy occurs when a single
egg divides after fertilization or when more than one egg is
fertilized. Twin fetuses usually result (over 65% of the time) from the
fertilization of two separate eggs; each baby has his or her own
placenta and amniotic sac. These are called fraternal twins or dizygotic (two zygotes) twins.
With fraternal twins, you can have a boy and a girl. Fraternal twins
occur in 1 out of every 100 births. These rates vary for different
races and areas of the world.
About 35% of the time, twins come from a
single egg that divides into two similar structures. Each has the
potential of developing into a separate individual. These are known as identical twins or monozygotic (one zygote) twins. Identical twins occur about once in every 250 births around the world.
Either or both processes may be involved
when more than two fetuses are formed. What we mean by that is triplets
may result from fertilization of one, two or three eggs, or quadruplets
may result from fertilization of one, two, three or four eggs.
A twin pregnancy that results from
fertility treatment most often results in fraternal twins. In some
cases of higher-number fetuses, a pregnancy resulting from fertility
treatment can result in fraternal and identical twins, when
more than one egg is fertilized (fraternal twins) and, in addition, one
or more of the eggs divides (identical twins).
The percentage of boys decreases slightly
as the number of babies increases. In other words, as the number of
babies a woman carries goes up, her chances of having more girls
increases.
Special Issues for Identical Twins. With identical twins, division of the fertilized egg occurs between the first few days and about day 8. If division of the egg occurs after 8 days, the result can be twins that are connected, called conjoined twins. (Conjoined twins used to be called Siamese twins.) These babies may share important internal organs, such as the heart, lungs or liver. Fortunately this is a rare occurrence.
Identical twins may face some risks. There’s a 15% chance they will develop a serious problem called twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome.
There is one placenta, and the babies’ blood vessels share the
placenta. The problem occurs when one baby gets too much blood flow and
the other too little.
Dad Tip
Together with your partner, make a list
of important telephone numbers and keep it with you. Include numbers
for your work, your partner’s work, the hospital, the healthcare
provider’s office, a back-up driver, baby-sitter or others. You may
also want to make a list of numbers of people you want to call after
the delivery of your baby. Take this list to the hospital with you.
There’s a chance that several different
types of diseases may occur in identical twins during their lifetimes.
This is less likely to happen with fraternal twins.
It may be important later in life for
your children to know whether they were identical or fraternal because
of health concerns. Before delivery, tell your healthcare provider you
would like to have the placenta(s) examined (with a pathology exam) so
you’ll know whether babies were identical or fraternal. It may be
valuable information in the future. Even if there are two placentas,
research shows it doesn’t mean twins are fraternal; nearly 35% of all
identical twins have two placentas.
The Frequency of Multiples.
The frequency of twins depends on the type of twins. Identical twins
occur about once in every 250 births around the world. It doesn’t seem
to be influenced by age, race, heredity, number of pregnancies or
medications taken for infertility (fertility drugs).
The incidence of fraternal twins is
influenced by race, heredity, mom’s age, the number of previous
pregnancies and the use of fertility drugs and assisted-reproductive
techniques. Twins occur in 1 out of every 100 pregnancies
in white women compared to 1 out of every 79 pregnancies in black
women. Certain areas of Africa have an incredibly high frequency of
twins. In some places, twins occur once in every 20 births. Hispanic
women also have a slightly higher number of twin births. The occurrence
of twins among Asians is less common—about 1 in every 150 births. In
Japan, only 6 sets of twins are born per 1000 births while in Nigeria
that rate is over 7 times greater. In Nigeria, fraternal twins are born
at a rate of 45 per 1000 births.
Heredity also plays a part. The incidence of twin births can run in families, on the mother’s
side. In one study of fraternal twins, the chance of a female twin
giving birth to a set of twins herself was about 1 in 58 births. The
study also showed if a woman is the daughter of a twin, she has a
higher chance of having twins. Another study reported 1 out of 24 (4%)
of twins’ mothers was a twin, but only 1 out of 60 (1.7%; about the
national average) of twins’ fathers was a twin.
If you’ve already given birth to a set of
fraternal twins, your chance of having another set of twins quadruples!
Other reasons for multiple fetuses include the use of fertility drugs,
in-vitro fertilization, women having babies later in life, some women
having more children, being very tall or obese, you recently
discontinued oral contraception or taking large doses of folic acid.
Women having babies later in life
accounts for nearly 35% of all multiple births. Age 30 seems to be the
magic age beyond which the number of multiple births increases. Over
70% of all multiple births are to women over age 30. In the United
States, the highest number of multiple births occurs in women over 40;
the next highest group is women between the ages of 30 and 39.
The increase in multiple births among
older women has been attributed to higher levels of gonadotropins. As a
woman ages, gonadotropin increases, and she’s more likely to produce
two or more eggs during one menstrual cycle. Most twin births in older
women are fraternal twins.
Having more children (or pregnancies) can
also result in more than one baby. This is true in all populations and
may be related to the mother’s age and hormone changes.
Some families are just more “blessed” than others. In one case we know of
personally, a woman had three single births. Her fourth pregnancy was
twins, and her fifth pregnancy was triplets! She and her husband
decided on another pregnancy; they were surprised (and probably
relieved) when that pregnancy resulted in only one baby.
Discovering You’re Carrying More than One Baby. Diagnosis of twins was more difficult before ultrasound was available.
It is uncommon to discover twin
pregnancies just by hearing two heartbeats. Many people believe when
they hear only one heartbeat, there could be no possibility of twins.
This may not be the case. Two rapid heartbeats may have a similar or
almost identical rate, which could make it difficult to know there are
two babies.
Measuring and examining your tummy during
pregnancy is important. Usually a twin pregnancy is noted during the
second trimester because you’re too big and growth seems too fast for
one baby. Ultrasound is the best way to diagnose a multiple pregnancy.
Do Multiple Pregnancies Have More Problems? With a multiple pregnancy, the possibility of problems goes up. Possible problems include the following:
• increased risk of miscarriage
• fetal death or mortality
• birth defects
• low birthweight or growth restriction
• pre-eclampsia
• problems with the placenta
• maternal anemia
• maternal bleeding or hemorrhage
• problems with the umbilical cord, including entwinement or tangling of the babies’ umbilical cords
• too much or too little amniotic fluid
• abnormal fetal presentations, such as breech or transverse lie
• premature labor
• difficult delivery and Cesarean delivery
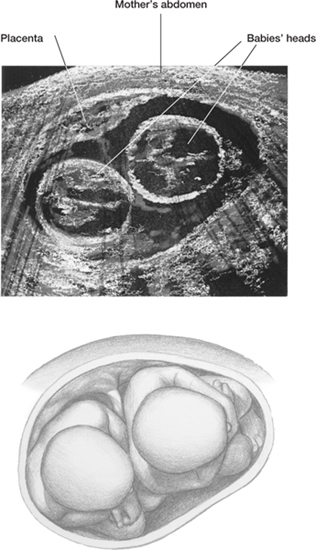
Ultrasound of twins shows two babies in the uterus.
If you look closely, you can see the two heads. The interpretive illustration shows how the babies are lying.
Birth defects are
more common among identical twins than fraternal twins. The incidence
of minor problems is twice as high as it is in a single pregnancy, and
major defects are also more common.
One of the biggest problems with multiple
pregnancies is premature delivery. As the number of babies increases,
the length of gestation and the birthweight of each baby decreases,
although this is not true in every case.
The average length of pregnancy for twins
is about 37 weeks. For triplets it’s about 35 weeks. For every week the
babies stay inside the uterus, their birth weights increase, along with
the maturity of organs and systems.
It’s important to continue your pregnancy
as long as possible; this may be achieved by bed rest. You may not be
able to carry on with regular activities for the entire pregnancy. If
your healthcare provider recommends bed rest, follow his or her advice.
Weight gain is important. You may be
advised to gain more than the normal 25 to 35 pounds, depending on the
number of babies you carry. With twins, if you were normal weight
before pregnancy, you may be advised to gain 40 to 54 pounds. For
overweight women, a weight gain between 31 and 50 pounds may be
recommended; for obese women, a gain between 25 and 42 pounds may be
recommended. If you’re expecting triplets, your weight gain may be
between 50 and 60 pounds.
Some researchers believe use of a tocolytic agent
(medication to stop labor), such as ritodrine, is critical in
preventing premature delivery. These medicines are used to relax the
uterus to keep you from going into premature labor.
Follow your healthcare
provider’s instructions closely. Every day and every week you can keep
the babies inside you are days or weeks you won’t have to visit them in
an intensive-care nursery while they grow, develop and finish maturing.