1. How Big Are You?
A condition that can make you grow too big too fast is a molar pregnancy, sometimes called gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN) or hydatidiform mole. A molar pregnancy develops from an abnormally fertilized egg.
When a molar pregnancy occurs, an embryo
does not usually develop. Abnormal placental tissue grows instead. The
most common symptom is bleeding during the first trimester. A woman may
have a lot of nausea and vomiting. Another symptom is the size of the
mother-to-be and how far along she is supposed to be in pregnancy. Half
the time, a woman is too large. Twenty-five percent of the time, she is
too small.
The most effective
way to diagnose molar pregnancy is by ultrasound. The ultrasound picture
has a “snowflake” appearance. The problem is usually found when the
test is done to find the cause of bleeding or rapid growth of the
uterus.
A molar pregnancy can become cancerous.
When it is diagnosed, surgery (dilatation and curettage [D&C]) is
usually done as soon as possible.
After a molar pregnancy,
effective birth control is important to be sure the molar pregnancy is
completely gone. Most healthcare providers recommend using reliable
birth control for at least 1 year before trying to get pregnant again.
2. How Your Baby Is Growing and Developing
The end of this week is the end of the
embryonic period. During the embryonic period, the baby has been most
susceptible to things that could harm it. Most birth defects occur then.
It’s good to know a vital part of your baby’s development is behind
you.
Few birth defects happen after this time.
However, drugs and other harmful exposures, such as severe stress or
radiation (X-ray), can hurt the baby at any time during pregnancy.
Continue to avoid them.
3. Changes in You
Emotional Changes
When pregnancy is confirmed, it can
affect you in many ways. Some women see pregnancy as a sign of
womanhood. Some consider it a blessing. Still others feel it’s a
problem. If you aren’t excited about pregnancy, don’t feel alone. It’s
common.
When and how you begin to regard the fetus
as a person is different for everyone. Some women say it’s when their
pregnancy test is positive. Others say it occurs when they hear the
fetal heartbeat, usually around 12 weeks. For still others, it happens
when they first feel their baby move, at between 16 and 20 weeks.
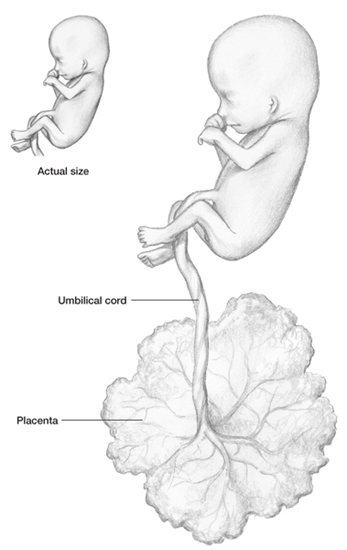
Baby is shown attached to the placenta by its
umbilical cord. Eyelids are fused and remain closed
until week 27 (fetal age—25 weeks).
You may find you are
emotional about many things. You may feel moody, cry at the slightest
thing or drift off in daydreams. Emotional swings are normal and
continue to some degree throughout your pregnancy.
Many pregnant women wonder why these
emotional changes happen. Most of the time, people tell them “it’s just
part of being pregnant.” But most often, it’s the hormones your body
makes during pregnancy. The changes can really affect your moods and
lead to forgetfulness and cloudy thinking.
Some emotions you feel may be caused by
other things. For example, if you cry and feel down for longer than 2
weeks, feel worthless or hopeless, or don’t take pleasure in most
things, you may be depressed. Be sure you discuss how you feel
emotionally with your healthcare provider.
Tip for Week 10
It’s common for your breasts to tingle
and to feel sore early in pregnancy. In fact, it may be one of the first
signs of pregnancy.
You can help yourself by getting
good prenatal care, and following your healthcare provider’s advice.
Keep all your prenatal appointments. Establish good communication with
your healthcare provider and the office staff. Ask questions. If
something bothers you or worries you, discuss it with someone reliable.