3. Multiple sclerosis
Two to four times more women than men suffer MS, which
happens when the immune system attacks the fatty (myelin) sheath covering
nerves. Symptoms often worsen at menopause and MS can be associated with severe
hot fushes.
Symptoms Variable, depending on the part of nervous
system affected, but they include fatigue, weakness, numbness, pins and needles
and other abnormal sensations, nerve pain, muscle spasms, blurred vision and
balance problems.
Treatments A whole range of treatments can reduce
infammation and treat symptoms, plus support from physiotherapists,
psychologists and other therapists. New biological agents have become available
in the past five years, and more are in the pipeline. Some consultants now
recommend vitamin D, as some studies suggest it may help prevent relapses.
4. Rheumatoid arthritis
Afecting two to four times as many women as men, the immune
system attacks the synovial membranes that surround joints, causing joint
destruction. It can also affect other tissues and organs, including eyes, skin,
lungs, liver and heart.
Symptoms Redness, swelling and pain in the joints
(often afecting matching joints on both sides of the body), morning stiffness,
fatigue, general feeling of unwellness (malaise).
Treatments Anti-infammatory and disease-modifying
drugs that slow underlying processes. Biological agents that directly target
joint infammation have made RA a much more treatable condition than it was even
five to ten years ago. The latest, rituximab, acts on the activity of immune
cells called B lymphocytes.
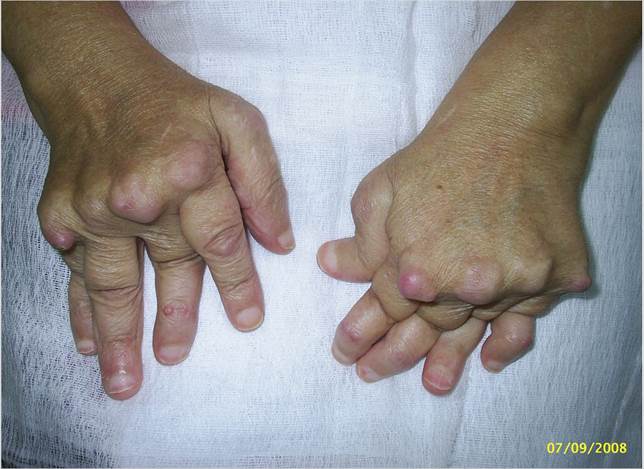
Biological agents
that directly target joint infammation have made rheumatoid arthritis a much
more treatable condition than it was even fve to ten years ago
5. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) are slightly
more likely to affect women than men.
Symptoms Abdominal pain, diarrhoea that is often
bloody, fatigue, weight loss, mouth ulcers.
Treatments Anti-infammatory drugs, steroids and
immune system suppressors. Surgery in severe cases. UC and Crohn’s have lagged
behind other autoimmune diseases but new treatments are in the pipeline. One
agent, vedolizumab, which blocks the transit of immune cells called leukocytes
from getting to the digestive tract, is already being used in the US and looks
promising, but isn’t yet approved in the UK.

Abdominal pain may
be the early symtom of IBD