Bladder
cancer
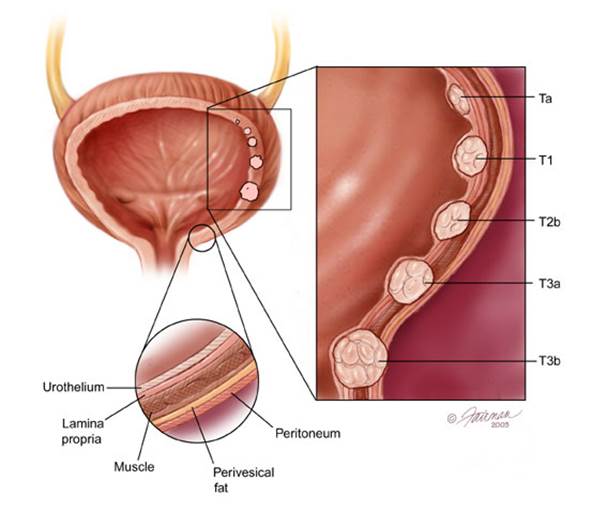
Most people don’t need to be screened
unless they are at high risk, because it has no tproved to be effective, and
most cancers found without screening are curable
·
Rating
2/5 for adults of all
ages
·
What’s involved
A test to check for
blood or cancer cells in urine.
·
Who needs it
Most people don’t need
to be screened unless they are at high risk, because it has no tproved to be
effective, and most cancers found without screening are curable
·
Risk factors
Smoking a family
history of the disease, and exposure to workplace chemicals.
Lung
cancer

Most don’t need the test unless they are
at the highest risk, because the cancer is uncommon in nonsmokers and the test
is not very accurate
·
Rating
2/5 for adults of all
ages
·
What’s involved.
A low-dose CT scan.
·
Who needs it
Most don’t need the
test unless they are at the highest risk, because the cancer is uncommon in
nonsmokers and the test is not very accurate
·
Risk factors
Smoking, a family
history of the disease, and long-term exposure to radon, asbestos, or arsenic.
Skin
cancer
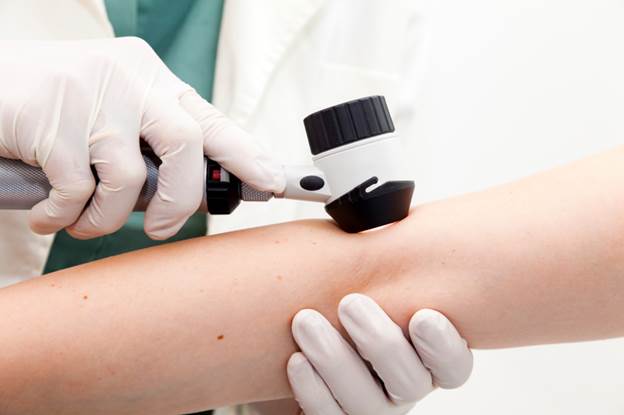
See a doctor if you notice suspicious
changes in the color, size, shape, or number of moles.
·
Rating
2/5 for adults of all
ages
·
What’s involved
A visual exam of your
skin by a physician looking especially for signs of melanoma, the deadliest
form of skin cancer.
·
Who needs it
Most adults don’t need
the exam unless they are at high risk, because the effectiveness of screening
has not been proved. But see a doctor if you notice suspicious changes in the
color, size, shape, or number of moles.
·
Risk factors
A family history of
melanoma, a personal history of frequent sunburns, a large or increasing number
of precancerous moles, and being fair-skinned or heavily freckled.
Oral
cancer

Keep away from risk factors: Smoking,
chewing tobacco, excessive alcohol consumption…
·
Rating
2/5 for adults of all
ages
·
What’s involved
A visual exam of the
mouth by a dentist or other health-care provider.
·
Who needs it
Most people don’t need
the test unless they are at high risk, because the cancer is relatively
uncommon.
·
Risk factors
Smoking, chewing
tobacco, excessive alcohol consumption, HPV infection, and weakened immunity
from medication, disease, or certain other causes.
Prostate
cancer
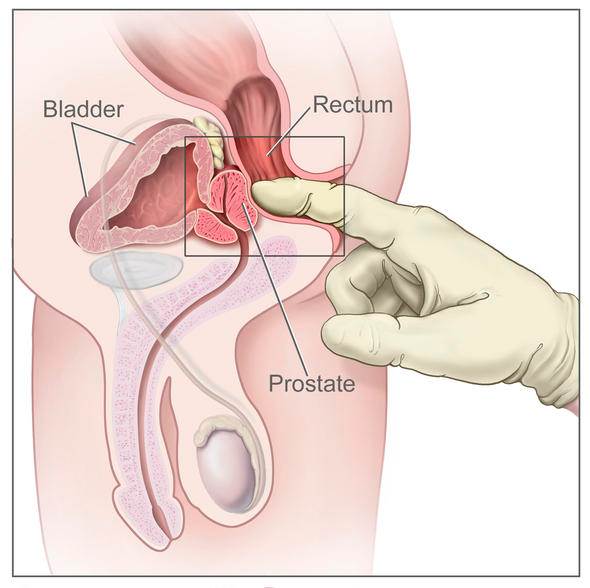
·
Ratings
2/5 for men age 50 to
74
1/5 for men of all
other ages
·
What’s involved
Prostate-specific
antigen (PSA) blood test.
·
Who needs it
Men age 50 to 74
should all with a doctor to see whether the benefits of the test outweigh the
harm for them based on their risk factors older men rarely need the test
because the cancer typically progresses so slowly that treatment does not
improve survival. Younger men should consider testing only if they are at high
risk, because the cancer is uncommon before age 50.
·
Risk factors
A family history of
the disease, being African-American, and smoking.
Ovarian
cancer
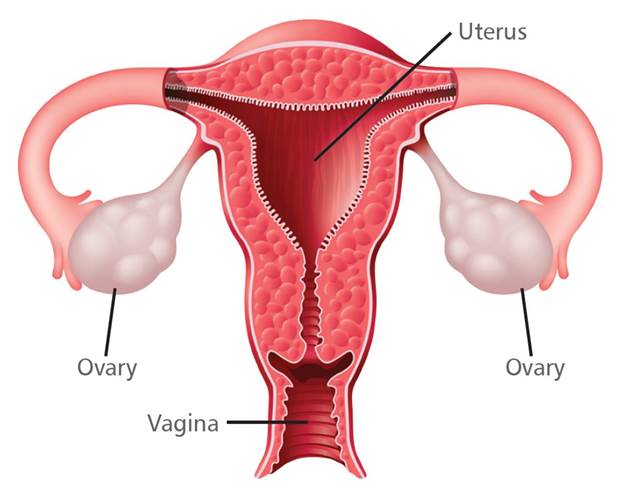
·
Ratings
1/5 for women of all
ages
·
What’s involved
A transvaginal
ultrasound or the CA-125 blood test, which measures a protein possibly
associated with ovarian cancer.
·
Who needs it
Women don’t need to be
tested unless they are at high risk, because neither test is likely to detect
the disease at a curable stage.
·
Risk factors
A family history of
ovarian, breast, or colon cancers, and possibly use of estrogen after menopause
for more than five years
Pancreatic
cancer
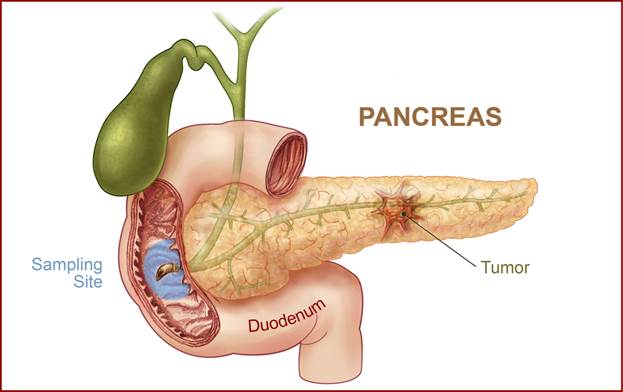
·
Rating
1/5 for adults of all
ages
·
What’s involved
Genetic tests or
imaging test of the abdomen
·
Who needs it
People don’t need to
be tested unless they are at high risk, because no test is likely to detect the
disease at a curable stage.
·
Risk factors
A family history of
the disease, smoking, obesity, and possibly type 2 diabetes.
Testicular
cancer
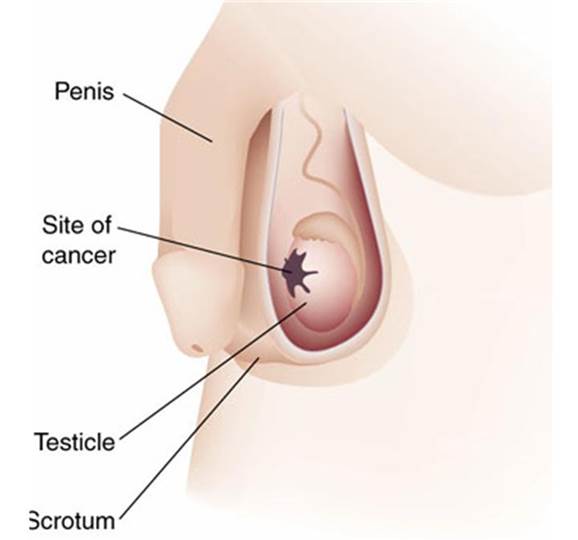
·
Rating
1/5 for men of all
ages
·
What’s involved
A physical exam of a
man’s testicles by a health-care professional.
·
Who needs it
Men don’t’ need to be
tested unless they are at high risk, because most cancers found without
screening are curable.
·
Risk factors
A family history, an
undescended testicle, or HIV infection.
Colon-cancer screening: just do it
Of the estimated
52,000 people who died of colorectal cancer last year, screening could have
saved more than half, according to the American Cancer Society. Yet around 40
percent of people 50 and older don’t get recommended screening tests
Not surprising, our
readers, who tend to be a health-savvy bunch, do better than that, according to
a survey of more than 10,000 subscribers 50 and older conducted by Consumer
Reports National Research Center. Eighty percent of them had been screened for
colon cancer in the last five years. But our survey also found worrisome gaps
in their knowledge of the tests used.

Success Story: For Tracy Doss,
colon-cancer screening allowed doctors to detect and remove precancerous
growths.
For example, less than
half of them were told what the test was looking for, about a third weren’t
told of potential complications and a quarter weren’t told what would happen if
the tests had abnormal results. Only 10 percent of people who had colonoscopy
or sigmoidoscopy, invasive forms of testing that use a scope to inspect the
colon, were told there was a simpler option. And only 55 percent were told of
the main risk of the procedures, a perforated colon.
Las, some patients got
tests that are not proved effective, including fecal DNA tests and CT
colonography (also called virtual colonoscopy). That’s unfortunate, because
there are a number of good colon-cancer tests to choose from. The chart below
shows the pros and cons of each.
|
Test
|
How it works
|
Cost
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
|
Colonoscopy
Every
10 years; starting at age 50. Sooner or more often for some high-risk people
or if result are abnormal.
|
Long,
flexible scope is passed through the rectum and entire colon to look for
polyps and tumors.
|
$1,120
|
Allows
immediate removal of polyps and biopsies; shows entire colon; needs to be
done just once a decade for most
|
Risk
of bowel infection, perforated bowel, and other complications; requires
full-day preparation with laxatives and dietary restriction; sedation
required; full-day recovery likely.
|
|
Flexible
sigmoidoscopy
every five years, with stool test (below) every three years.
|
Short,
flexible scope is inserted into the lower colon to look for polyps and
tumors.
|
$740
|
No
sedation required; can return to work same day; simpler bowel preparation
than for colonoscopy; fewer complications than for colonoscopy
|
Colonoscopy
required if positive; shows only the lower third of the colon, so not as
thorough as colonoscopy
|
|
Stool
testing (immunochemical or guaiac-based) Every year.
|
Detects
traces of blood in stool from tumors and polyps that tend to bleed
|
$5
to $25
|
Noninvasive;
lowest risk of complications; samples are taken at home.
|
Colonoscopy
required if positive; can’t detect most polyps; requires yearly testing; some
people might find the test unpleasant.
|
Risks and benefits of two tests
The data below show
that the risks of prostate-cancer screening probably outweigh the benefits and
that the benefits of breast-cancer screening are smaller than many women may
suspect.
Prostate
cancer
Screening 1,000 men
every open to four years from age 55 to 69 results in:
·
0
to 1 prostate-cancer deaths prevented
·
3
serious complications caused by treating the cancer, including death, heart
attacks, and blood clots in the legs or lungs
·
40
men becoming impotent or incontinent from treatment complications
Breast cancer
Screening 1,000 women
every two years from age 50 to 69 results in:
·
5
breast-cancer deaths prevented
·
780
false-positive results
·
55
unneeded biopsies
An unknown number of complications
from breast-cancer treatment, including infection, nausea, and exposure to
radiation, which may itself cause cancer. Starting screening at age 40 instead
of 50 will prevent one additional death but cause an additional 470 false
positives and an additional 33 unneeded biopsies