Super juices, energy shots, vitamin-infused
nutrition bars – grocery stores teem with foods that have been pumped up with
nutrients during processing. A 12 ounce bottle of Odwalla Superfood Blueberry B
Premium Fruit Smoothie Blend, for example, delivers up to 530 percent of the
recommended daily value of the B vitamins thiamin, riboflavin, B6, and B12.
Too
Much Of A Good Thing? That’s good, right? Not necessarily
That’s good, right? Not necessarily. Eat
enough fortified food s in a day-especially along with a multivitamin o a
single-ingredient supplement like calcium-and you could end up not only with
more of an ingredient than you need but also more than is good for you.
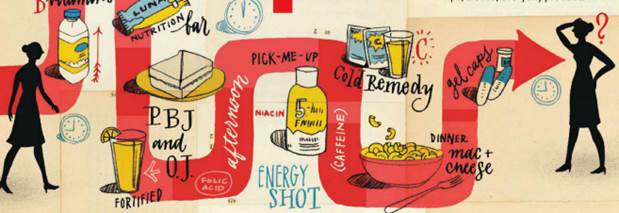
We calculated how much caffeine, calcium,
folate, and vitamin C a person might consume in a day. All of those can have
undesirable effects in very high doses (see the table a left). Our hypothetical
consumer breakfasted on coffee, cereal, orange juice, a multivitamin, and a
couple of calcium chews; snacked on a nutrition bar; lunched on a
peanut-butter-and-jelly sandwich and lemonade; snacked on a protein shake; had
an energy shot as an afternoon pick-me-up; dined on mac and cheese; and took two
packets of a cold remedy and a couple of headache gel caps at various times
during the day.
The risk you run
Caffeine

·
Most adults can safely consume up to 400
milligrams a day; pregnant women up to 200 milligram.
·
Risk of too much: jitters, insomnia, rapid heart
rate, abnormal heart rhythm, increased blood pressure.
Calcium

·
Recommended daily value: 1000 to 1200
milligrams.
·
Upper limit: 2000 to 2500 milligrams.
·
Risks of too much over time: constipation,
kidney stones, impaired absorption of iron and zinc.
Folate:
·
Recommended daily value: 400 micrograms.
·
Upper limit: 1000 Micrograms.
·
Risks of too much over time: masking of B12
deficiency, which causes nerve damage. Deficiency is most common in people 50
or older of vegetarians.
Vitamin
C

·
Recommended daily value: 60 mg.
·
Upper limit: 2000 mg
·
Risks of too much: diarrhea, nausea, vomiting,
heartburn abdominal cramps, bloating.
The day’s tally
Here’s what out nutrient-rich consumer took
in : 537 milligrams of caffeine( more than 200 milligrams too much); 376
percent of the recommended daily value of calcium; 3,952 percent of the
recommended daily value of vitamin C; and 540 percent of the recommended daily
value of folate.
Ingredients other than those we’ve highlighted
can cause problems, too. Some studies have linked high blood levels of iron to
an elevated risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes, and iron supplements van
interfere with the body’ absorption of zinc. Too much vitamin A can cause
birth defects and liver damage.
Some of the products we sued in our
calculations have other extras: the 5-hour Energy Extra Strength shot our
consumer drank (242 milligrams of caffeine) also has 200 percent of the daily
value of niacin, 2,000 percent of vitamin B6, and 8,333 percent of vitamin B12.
Bottom
line.
A balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables,
low-fat dairy products, lean protein, whole grains, and legumes should provide
all you need of major vitamins and minerals, plus fiber and a rainbow of
healthful phytochemicals. If you eat a restricted diet of need more of certain
nutrient, a multivitamin or individual supplement can plug the gaps. To avoid
becoming over fortified, read labels on processed foods. Although manufacturers
don’t have to list caffeine levels, they must list amounts of added vitamins
and minerals.